How to combat pests in houseplants?
Last reviewed: 11.03.2025

Houseplants not only beautify interiors but also improve air quality, contribute to creating a cozy atmosphere, and have a positive impact on our mental health. However, despite all their benefits, houseplants can become targets for various pests. These pests not only damage the appearance of plants but can also lead to their death by disrupting their health. In this article, we will explore how to effectively combat pests in houseplants, prevent their appearance, and ensure the healthy growth of your green companions.
Common pests in houseplants
Aphids
- Description: Small insects, often green or black, that feed on plant juices.
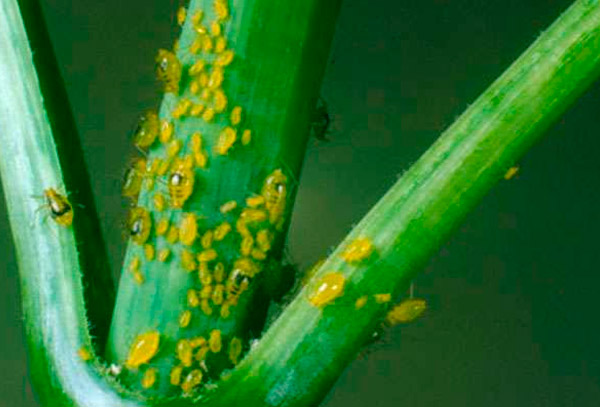

- Signs of Infestation:
- Sticky honeydew on leaves and stems.
- Curling and yellowing of leaves.
- Development of black spots due to aphids.
- Damage: Aphids weaken the plant, transmit viruses, and promote the growth of mold.
Spider mites
- Description: Tiny insects that leave fine webs on leaves and stems.
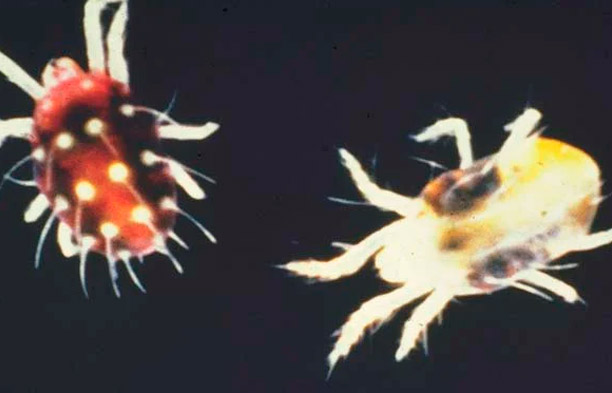
- Signs of Infestation:
- Spots on leaves, which may be yellow, brown, or white.
- Leaves become dry and brittle.
- Presence of webs, especially on the undersides of leaves.
- Damage: Weakens the plant, reduces photosynthesis, and accelerates wilting.
Scale insects
- Description: Insects with a hard shell that attach to stems and leaves.
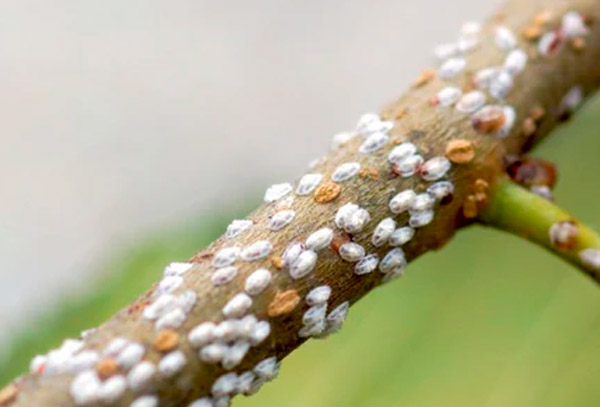

- Signs of Infestation:
- White or brown insects on the surface of leaves.
- Slow wilting and yellowing of leaves.
- Damage: They feed on plant juices, causing a nutrient deficiency.
Mealybugs
- Description: Small white or grayish insects covered with a cotton-like substance.

- Signs of Infestation:
- Cotton-like substance on leaves, stems, and roots.
- Slowed plant growth and yellowing of leaves.
- Damage: Draws sap from plants, leading to weakening and death.
Whiteflies
- Description: Small white-winged insects resembling mosquitoes.
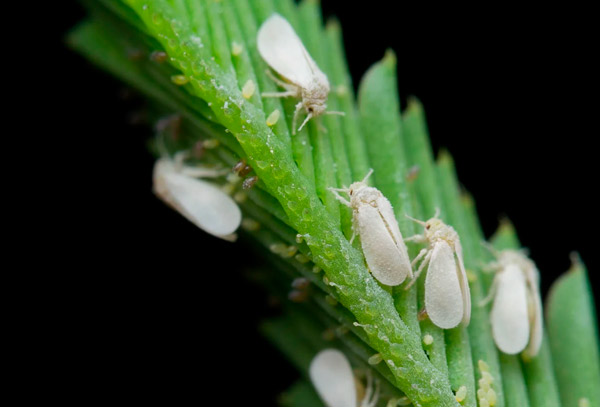

- Signs of Infestation:
- Small white insects on leaves and stems.
- Powdery residue on leaves and soil.
- Damage: Feeds on plant juices and may transmit viruses.
Powdery mildew and other fungal pests
- Description: Fungal infections that appear as white powder on leaves and stems.

- Signs of Infestation:
- White coating on leaves, especially in shaded areas.
- Wilting and yellowing of leaves.
- Damage: Disrupts photosynthesis and contributes to plant death.
Causes of pest infestation
- Improper Growing Conditions:
- Lack or excess of light.
- Incorrect watering regime.
- Temperature fluctuations that weaken plants.
- Poor Sanitation:
- Contaminated tools and pots.
- Frequent moving of plants, which causes stress.
- Importing Plants:
- New plants may introduce pests.
- Stressful Conditions for Plants:
- Weak growth and fatigue make plants more vulnerable to pests.
Pest prevention
- Proper Plant Care:
- Ensure optimal lighting, watering, and temperature conditions for plants.
- Regularly clean leaves of dust and dead parts.
- Sterilization of Tools:
- Treat gardening tools with disinfectants before use to prevent pest spread.
- Quarantine New Plants:
- Isolate new plants for a few weeks before bringing them into the main interior and thoroughly inspect them for pests.
- Using Repellents and Natural Barriers:
- Spray soapy solutions or use essential oils to prevent pest appearance.
Methods of combatting pests
- Mechanical Methods:
- Manual Removal: Gently remove pests from leaves and stems using a cotton swab soaked in alcohol.
- Traps: Yellow sticky traps attract and capture pest insects.
- Chemical Methods:
- Systemic Insecticides: Absorbed by the plant and kill pests from the inside. Suitable for severe infestations.
- Contact Insecticides: Apply directly to affected plant areas. Effective for light to moderate infestations.
- Safety: Follow the manufacturer's instructions when using chemical treatments. Wear gloves and ensure good ventilation.
- Organic and Natural Methods:
- Nematodes: Beneficial microorganisms that destroy pests in the soil.
- Natural Insecticides: Soap solution, neem oil, garlic infusion, and other natural remedies effectively combat pests.
- Biodiversity: Introduce beneficial insects, such as ladybugs, to feed on pests.
- Hybrid Methods:
- Combination of Methods: Using several methods together increases their effectiveness and prevents pests from developing resistance.
Home remedies for pests
- Soapy Solution:
- Mix 1 tablespoon of liquid soap with 1 liter of water. Spray on affected plant areas. Repeat every 7 days until pests are gone.
- Neem Oil:
- Dilute neem oil as instructed on the packaging. Spray on leaves and stems. Neem oil effectively combats aphids, scale insects, and spider mites.
- Garlic Infusion:
- Crush 3-4 garlic cloves, pour 1 liter of boiling water, and steep for 24 hours. Strain and spray on plants. Garlic has natural insecticidal properties.
- Vinegar Solution:
- Mix 1 tablespoon of white vinegar with 1 liter of water. Spray on affected areas, avoiding contact with leaves. Vinegar helps fight aphids and other pests.
Post-treatment care
- Washing Plants:
- After applying insecticides, rinse the leaves with water to remove residues and prevent buildup.
- Monitoring Plant Health:
- Regularly inspect plants for pests and signs of recurrence. Repeat treatments if necessary.
- Strengthening Plant Immunity:
- Feed plants with balanced fertilizers to ensure they get the necessary nutrients and enhance resistance to pests.
Specific recommendations for different types of plants
- Flowering Plants (Orchids, Geraniums, Philodendrons):
- Often suffer from aphids and powdery mildew. Use soapy solutions or neem oil for treatment.
- Provide good ventilation to prevent fungal development.
- Green Leafy Plants (Pachira, Sansevieria, Zamioculcas):
- These plants can tolerate lower humidity but still require regular care.
- Use natural insecticides and maintain clean leaves.
- Succulents and Cacti:
- Less susceptible to pests due to their tough foliage but may suffer from spider mites.
- Use dry methods like alcohol treatment or isolate the infected plant.
- Tropical Plants (Spathiphyllum, Ficus Benjamin):
- Often infected with spider mites and powdery mildew.
- Use regular water spraying or soapy solution to prevent infestation.
Professional help and consultation
- When to Consult Experts:
- If pest infestation has spread to all parts of the plant.
- If home remedies and regular treatments are ineffective.
- When plants begin to wilt quickly and show signs of severe stress.
- Services Offered by Professionals:
- Inspection and diagnosis of plant condition.
- Application of professional insecticides and fungicides.
- Recommendations for ongoing care and prevention.
Conclusion
Combating pests in houseplants requires attention to detail and regular care. Understanding the types of pests, their behavior, and the methods to control them will help keep your plants healthy and avoid serious problems. By using a combination of preventive measures and effective pest control methods, your green companions will always thrive and remain beautiful. Regular monitoring and timely responses to pest appearance are crucial. With proper care, your houseplants will flourish for many years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the most common pests of houseplants? The most common pests are aphids, spider mites, scale insects, mealybugs, whiteflies, and fungal pathogens such as powdery mildew.
How can you distinguish pests from plant diseases? Pests usually appear as insects or their traces on plants, such as sticky honeydew, spots, or webs. Diseases are more often expressed as spots, wilting, or changes in leaf color without visible insects.
Can pests be completely eradicated without using chemicals? Yes, there are effective organic and natural methods for pest control, such as soapy solutions, neem oil, garlic infusions, and mechanical removal of pests. It is important to combine different methods for the best results.
How often should preventive treatments for plants be carried out? Regular preventive treatments are recommended every 2-4 weeks, especially during the plants' active growth periods. This will help prevent the appearance of pests and diseases.
Which plants are less prone to pests? Some plants, such as Sansevieria, Zamioculcas, Kalanchoe, and succulents, are less prone to pests due to their tough foliage and ability to withstand adverse conditions.
Final Tips:
- Regular Inspection: Frequently check your plants for pests, especially new and recently repotted plants.
- Room Cleanliness: Maintain cleanliness around your plants, remove fallen leaves and debris to prevent pest development.
- Proper Nutrition: Healthy plants are more resistant to pests. Ensure regular fertilizing and proper watering schedules.
- Isolate Infected Plants: If one plant is infected, isolate it from the others to prevent pest spread.
By following these recommendations, you can effectively combat pests and maintain the health of your houseplants, enjoying their beauty and life in your home.
